Dr Ahsan Tariq , MBBS, MRCP (UK ) ongoing, IMT ( Internal Medicine Trainee, NHS England), GMC : 7805049
Dr Ahsan Tariq is a UK-registered medical doctor with a background in internal medicine and a focus on evidence-based research in cognitive health and nootropics. He critically reviews scientific studies, supplements, and ingredients to help readers make informed, safe, and effective choices for brain health and performance.
Introduction:
Hydration Hacks: Water is one of the most essential nutrients for the human body, yet many people struggle to drink enough of it daily. Despite its simplicity, proper hydration plays a powerful role in energy levels, digestion, mental clarity, skin health, and overall well-being. Modern lifestyles, busy routines, and constant screen time often push hydration to the background, leading to fatigue, headaches, and reduced focus.
This comprehensive guide explores hydration hacks practical, science-backed strategies that make drinking more water effortless and sustainable. From understanding why hydration matters to simple daily habits that increase water intake naturally, this article covers everything you need to stay consistently hydrated.
Understanding Hydration And Why It Matters
Hydration refers to maintaining the correct balance of fluids in the body. Since the human body is composed of approximately 60% water, even mild dehydration can disrupt essential bodily functions [1].
The Role Of Water In The Body
Water supports nearly every physiological process, including:
- Regulating body temperature
- Transporting nutrients and oxygen
- Supporting digestion and metabolism
- Lubricating joints and tissues
- Removing waste and toxins
According to research, water is involved in cellular function, blood circulation, and brain performance, making hydration critical for both physical and mental health [2].
How Much Water Do You Really Need?
There is no one-size-fits-all rule for water intake. Needs vary based on age, activity level, climate, and overall health. However, general recommendations suggest:
- Men: ~3.7 liters per day
- Women: ~2.7 liters per day
This includes fluids from beverages and food sources [3].
Signs And Symptoms Of Dehydration
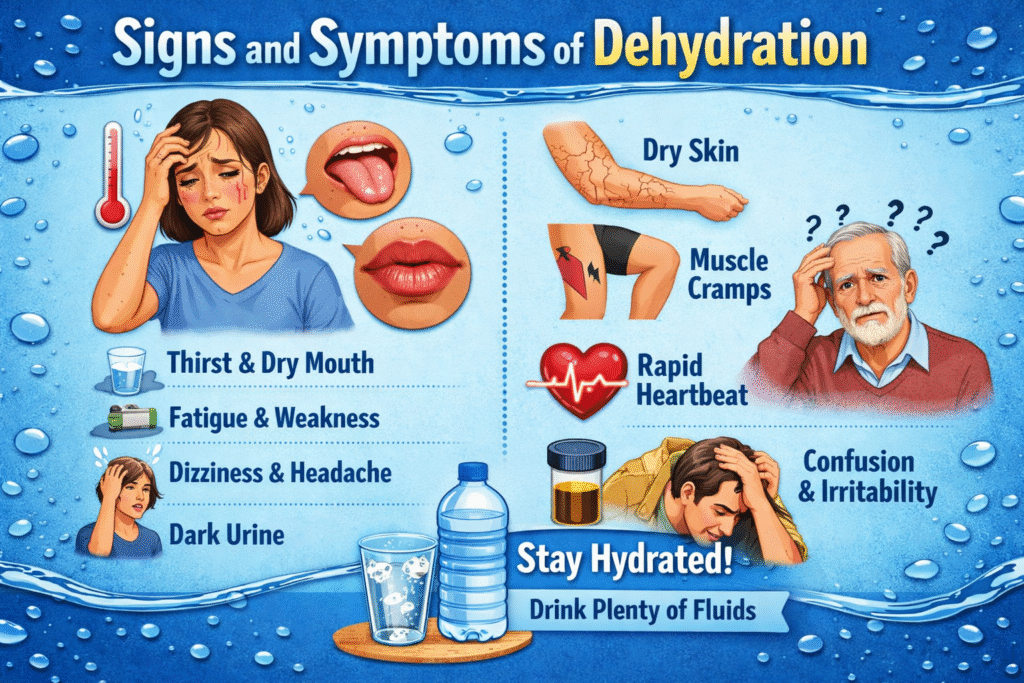
Many people underestimate dehydration because its early symptoms are subtle.
Common Physical Symptoms
- Dry mouth and lips
- Fatigue or low energy
- Headaches
- Dark yellow urine
- Dizziness
Even mild dehydration can impair physical performance and mood, according to studies [4].
Cognitive And Mental Effects
Dehydration affects brain function significantly. Research shows that reduced hydration levels can impact attention, memory, and reaction time [5].
Benefits Of Drinking More Water Daily
Increasing daily water intake provides measurable benefits across multiple systems in the body.
Improved Energy Levels
Water helps transport oxygen and nutrients to cells, supporting energy production. Studies link dehydration with increased fatigue and reduced endurance [6].
Better Digestion And Gut Health
Adequate hydration supports saliva production, stomach acid balance, and intestinal movement, reducing constipation and bloating [7].
Enhanced Skin Health
Proper hydration contributes to skin elasticity and barrier function. While water alone doesn’t eliminate skin issues, it supports overall skin health [8].
Weight Management Support
Drinking water before meals may promote fullness and reduce calorie intake, according to multiple controlled trials [9].
Hydration Hacks: Simple Ways To Drink More Water Daily
Building hydration habits doesn’t require drastic changes. Small, consistent actions can make a significant difference.
Start Your Day With Water
Drinking water first thing in the morning helps:
- Rehydrate after overnight fluid loss
- Kick-start metabolism
- Improve alertness
According to health experts, morning hydration supports better daily intake patterns [10].
Use Visual Reminders
Keeping a water bottle visible increases the likelihood of frequent sipping. Studies show that environmental cues strongly influence habit formation [11].
Set Hydration Goals
Instead of vague intentions, set clear goals like:
- One glass every hour
- One bottle before lunch
Goal-setting has been proven to improve health behavior adherence [12].
Flavoring Water Naturally
Many people dislike plain water. Adding natural flavors can make hydration enjoyable.
Healthy Flavor Options
- Lemon or lime slices
- Cucumber and mint
- Berries or orange slices
- Ginger or basil
These additions enhance taste without added sugar, making water more appealing [13].
Avoid Sugary Alternatives
Replacing water with sugary drinks increases calorie intake and may worsen dehydration due to diuretic effects [14].
Smart Hydration Through Food
Hydration isn’t limited to drinking water alone.
Water-Rich Foods
Fruits and vegetables contribute significantly to fluid intake.
| Food | Water Content (%) |
|---|---|
| Cucumber | 96% |
| Watermelon | 92% |
| Oranges | 86% |
| Strawberries | 91% |
| Lettuce | 95% |
According to nutrition research, food can provide up to 20% of daily fluid needs [15].
Hydration At Work And School
Busy environments often lead to neglected hydration.
Desk Hydration Hacks
- Keep a refillable bottle at your desk
- Drink water before meetings
- Pair water intake with breaks
Workplace studies show hydration improves concentration and productivity [16].
Hydration For Students
Children and teens often fail to meet hydration needs. Research links proper hydration with improved attention and memory in academic settings [17].
Technology And Hydration Tracking

Modern tools make hydration tracking easier.
Hydration Apps And Smart Bottles
Apps remind users to drink water and track intake. Studies show digital reminders significantly improve hydration compliance [18].
Wearable Devices
Fitness trackers often include hydration prompts based on activity levels, helping users stay balanced during workouts [19].
Hydration During Exercise
Physical activity increases fluid loss through sweat.
Pre-Workout Hydration
Drinking water before exercise improves endurance and reduces injury risk [20].
Post-Workout Rehydration
Replenishing fluids after workouts helps restore electrolyte balance and muscle recovery [21].
Seasonal Hydration Needs
Hydration requirements change with weather conditions.
Summer Hydration
Hot weather increases sweat loss, making frequent water intake essential [22].
Winter Hydration
Cold weather reduces thirst sensation, increasing dehydration risk despite lower temperatures [23].
Common Hydration Myths
Myth 1: Thirst Is The Best Indicator
Thirst often appears after dehydration has already begun [24].
Myth 2: Coffee Causes Severe Dehydration
Moderate caffeine intake does not significantly dehydrate the body, according to recent research [25].
Building Sustainable Hydration Habits
Consistency is more important than perfection.
Habit Stacking Technique
Pair drinking water with existing habits, such as:
- Drinking water after brushing teeth
- Having water with every meal
Behavioral science supports habit stacking for long-term change [26].
Make Hydration Enjoyable
Choosing bottles you like and experimenting with flavors increases adherence [27].
Hydration For Special Populations
Older Adults
Aging reduces thirst sensitivity, increasing dehydration risk. Regular reminders are essential [28].
Children And Teens
Proper hydration supports growth, cognitive development, and physical activity [29].
Long-Term Health Impact Of Proper Hydration
Chronic dehydration is linked to kidney stones, urinary tract infections, and metabolic issues. Maintaining hydration supports long-term health and disease prevention [30].
Conclusion: Small Hydration Changes, Big Health Benefits
Hydration doesn’t need to be complicated. By applying simple hydration hacks like starting your day with water, using reminders, choosing water-rich foods, and tracking intake you can significantly improve daily hydration. Over time, these small habits support better energy, focus, digestion, and overall wellness.
Staying hydrated is one of the easiest yet most powerful health decisions you can make every day.
References
- According to the National Academies of Sciences on body water composition
- Research on cellular hydration and metabolism
- Institute of Medicine daily fluid intake guidelines
- Studies on dehydration symptoms and performance
- Cognitive performance research on hydration
- Energy metabolism and hydration studies
- Digestive health and fluid intake research
- Skin barrier and hydration studies
- Water intake and appetite control trials
- Morning hydration behavioral studies
- Environmental cue and habit research
- Goal-setting theory in health behaviors
- Nutrition studies on flavored water intake
- Sugar-sweetened beverage research
- Food-based hydration contribution studies
- Workplace hydration productivity studies
- School hydration and learning research
- Mobile health app hydration studies
- Wearable hydration tracking research
- Sports hydration guidelines
- Exercise recovery hydration studies
- Heat exposure and hydration research
- Cold climate dehydration studies
- Thirst mechanism research
- Caffeine and hydration studies
- Habit formation psychology research
- Behavioral adherence studies
- Aging and hydration sensitivity research
- Pediatric hydration studies
- Chronic dehydration and disease risk research

