Dr Ahsan Tariq , MBBS, MRCP (UK ) ongoing, IMT ( Internal Medicine Trainee, NHS England), GMC : 7805049
Dr Ahsan Tariq is a UK-registered medical doctor with a background in internal medicine and a focus on evidence-based research in cognitive health and nootropics. He critically reviews scientific studies, supplements, and ingredients to help readers make informed, safe, and effective choices for brain health and performance.
Introduction
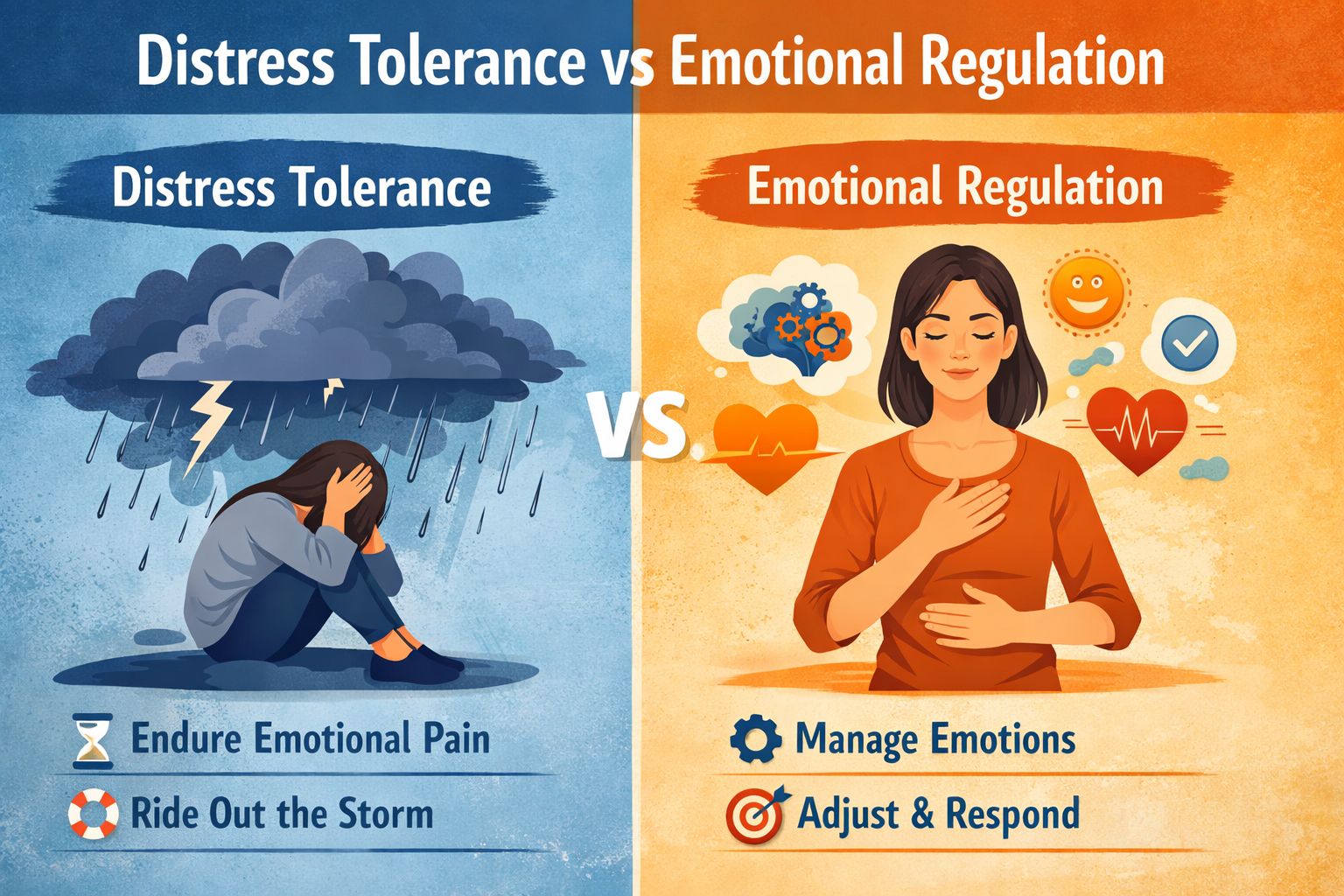
Mental health skills are increasingly recognized as essential tools for navigating stress, uncertainty, and emotional challenges in daily life. Among the most frequently discussed concepts in modern psychology are distress tolerance and emotional regulation. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they represent distinct psychological processes with different purposes, mechanisms, and outcomes. Understanding the difference between distress tolerance vs emotional regulation is critical for choosing appropriate coping strategies, therapy approaches, and self-care techniques.
Both concepts play a central role in cognitive behavioral therapy, dialectical behavior therapy, and emotional intelligence research. However, misuse or misunderstanding of these skills may reduce their effectiveness or even exacerbate emotional difficulties. This article provides a detailed, science-backed comparison designed for beginners and professionals alike, while maintaining clinical accuracy and SEO best practices.
Understanding The Topic
What Is Distress Tolerance
Distress tolerance refers to an individual’s ability to endure emotional discomfort without attempting to escape, suppress, or immediately change the experience. It emphasizes surviving emotional pain rather than eliminating it. This concept is a core component of dialectical behavior therapy, originally developed for individuals experiencing intense emotional sensitivity [1].
Distress tolerance does not aim to make a person feel better instantly. Instead, it teaches skills that help prevent impulsive reactions when emotions feel overwhelming. According to clinical psychology research, distress tolerance is especially useful during crises or situations that cannot be immediately resolved [2].
What Is Emotional Regulation
Emotional regulation is the process of identifying, understanding, managing, and modifying emotional responses in a flexible and goal-oriented manner. It involves both conscious and unconscious strategies that influence emotional intensity, duration, and expression [3].
Emotional regulation skills allow individuals to adapt emotions to fit situational demands. These skills are fundamental to mental health, social functioning, and decision-making. Research shows that effective emotional regulation is associated with better psychological well-being and interpersonal relationships [4].
How It Works
Mechanisms Of Distress Tolerance
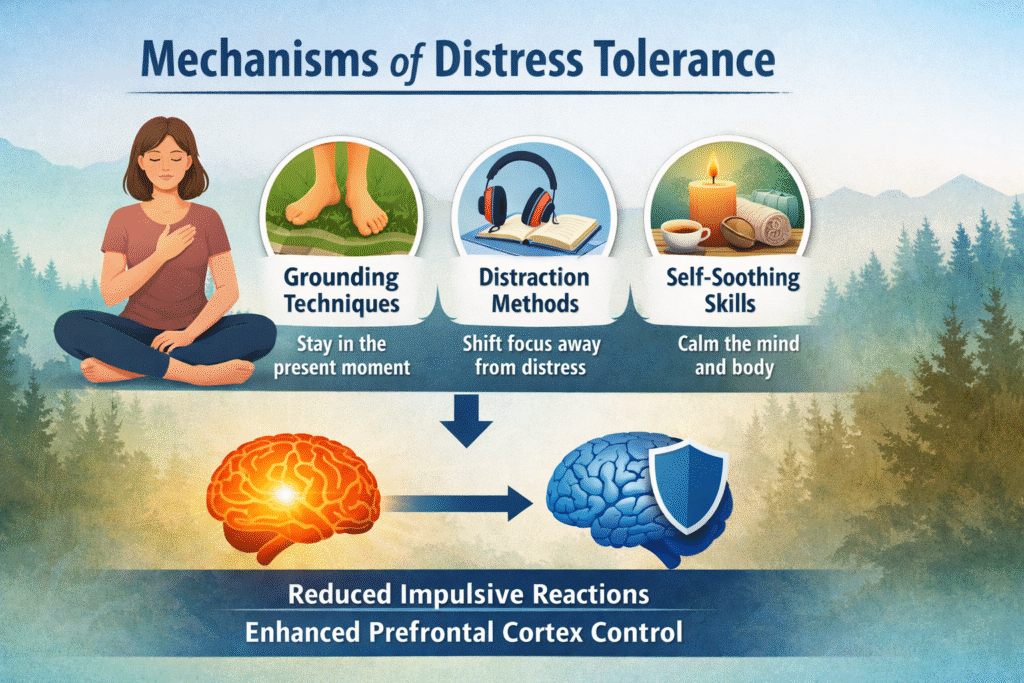
Distress tolerance works by increasing psychological endurance during emotional distress. Instead of avoiding discomfort, individuals practice acceptance-based strategies such as grounding, distraction, and self-soothing. Neurobiological studies suggest that these techniques reduce impulsive behaviors by strengthening prefrontal cortex control over emotional reactivity [5].
These skills are particularly useful when emotions are intense and cognitive problem-solving is temporarily impaired [6].
Mechanisms Of Emotional Regulation
Emotional regulation operates through cognitive, behavioral, and physiological pathways. Strategies such as cognitive reappraisal, emotional labeling, and attentional control help modify emotional responses before they escalate [7].
Brain imaging research indicates that emotional regulation activates neural circuits associated with executive function, enabling individuals to modulate emotional responses more effectively [8].
Importance
Why Distress Tolerance Matters
Low distress tolerance has been linked to anxiety disorders, substance misuse, and emotional dysregulation [9]. Individuals who struggle to tolerate distress may engage in avoidance or impulsive coping behaviors. Distress tolerance skills help reduce these risks by promoting emotional stability during high-stress situations [10].
Why Emotional Regulation Matters
Emotional regulation is foundational to mental resilience, academic performance, and social competence. Poor emotional regulation is associated with mood disorders, interpersonal conflict, and chronic stress [11]. Developing regulation skills enhances emotional awareness and adaptive functioning across life domains [12].
Proven Benefits
Benefits Of Distress Tolerance
Distress tolerance skills help individuals remain functional during emotional crises. Research demonstrates that improved distress tolerance reduces emotional reactivity and harmful coping patterns [13]. These skills are especially effective for managing acute stress, grief, and high emotional arousal.
Benefits Of Emotional Regulation
Emotional regulation improves psychological flexibility and long-term emotional health. Studies show that individuals with strong regulation skills experience lower levels of depression, anxiety, and emotional exhaustion [14]. Emotional regulation also enhances problem-solving and relationship satisfaction [15].
Potential Risks
Risks Of Distress Tolerance
Overreliance on distress tolerance may lead to emotional suppression if used excessively. Some researchers caution that enduring distress without processing emotions can delay emotional resolution [16]. Distress tolerance should not replace emotional understanding or therapeutic intervention when needed.
Risks Of Emotional Regulation
Excessive emotional control can result in emotional inhibition or reduced emotional authenticity. Research indicates that habitual emotional suppression is linked to increased physiological stress and reduced emotional clarity [17].
Scientific Evidence
Distress tolerance has been extensively studied within the framework of dialectical behavior therapy. Controlled trials demonstrate its effectiveness in reducing emotional instability and maladaptive coping behaviors [18].
Emotional regulation research spans neuroscience, developmental psychology, and clinical psychology. Longitudinal studies show that emotional regulation predicts mental health outcomes across the lifespan [19].
Benefits Vs Risks Comparison
| Aspect | Distress Tolerance | Emotional Regulation |
|---|---|---|
| Primary goal | Survive emotional pain | Modify emotional responses |
| Best used during | Crisis situations | Daily emotional management |
| Main benefit | Reduced impulsive reactions | Improved emotional flexibility |
| Main risk | Emotional avoidance | Emotional suppression |
Benefits Vs Risks Table
| Skill | Key Benefits | Potential Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Distress tolerance | Crisis stability, impulse control | Emotional stagnation |
| Emotional regulation | Emotional balance, adaptability | Overcontrol of emotions |
Safe Usage Guidelines
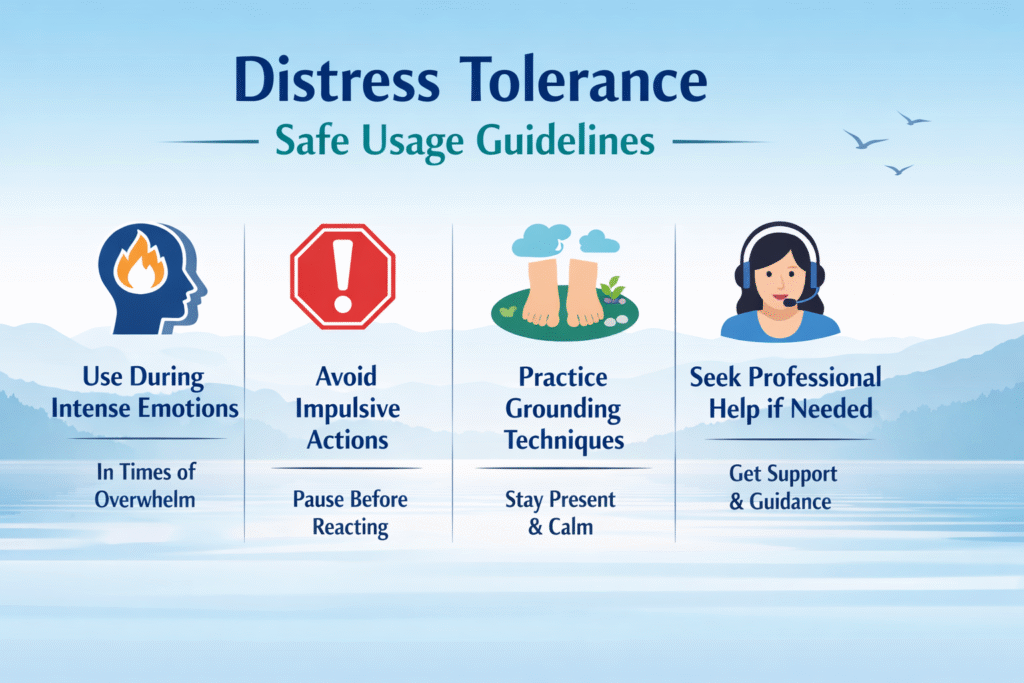
Distress tolerance should be applied during moments of emotional overwhelm when immediate emotional change is unrealistic [20]. Emotional regulation techniques are most effective when emotions are manageable enough for reflection and adjustment [21].
Mental health professionals recommend using both skills complementarily rather than exclusively [22].
Who Should Avoid It
Individuals with unresolved trauma may find distress tolerance challenging without professional support [23]. Similarly, emotional regulation strategies may be less effective during acute emotional crises and should not be forced in such moments [24].
Alternatives
Alternative approaches include mindfulness-based stress reduction, acceptance and commitment therapy, and compassion-focused therapy. These methods integrate both acceptance and emotional awareness principles [25].
Expert Opinions
Clinical psychologists emphasize that distress tolerance and emotional regulation are not competing skills but sequential ones. Experts suggest tolerating distress first, then regulating emotions once stability is achieved [26]. This approach aligns with modern integrative therapy models [27].
Key Takeaways
Distress tolerance focuses on enduring emotional pain safely, while emotional regulation emphasizes modifying emotional responses. Both skills are essential for emotional health and should be practiced together for optimal results [28].
FAQs
Is distress tolerance better than emotional regulation
Neither is superior. Each serves a different psychological purpose depending on emotional intensity [29].
Can both skills be learned
Research confirms that both distress tolerance and emotional regulation skills can be developed through structured training and practice [30].
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between distress tolerance vs emotional regulation empowers individuals to respond more effectively to emotional challenges. Distress tolerance provides stability during emotional storms, while emotional regulation enables long-term emotional balance. When used together, these skills form a comprehensive framework for emotional resilience, mental well-being, and adaptive coping.
References
- Linehan MM, 1993
- Simons JS, Gaher RM, 2005
- Gross JJ, 1998
- Gross JJ, John OP, 2003
- Ochsner KN et al., 2002
- Koole SL, 2009
- Gross JJ, Thompson RA, 2007
- Buhle JT et al., 2014
- Leyro TM et al., 2010
- Anestis MD et al., 2012
- Aldao A et al., 2010
- Thompson RA, 2011
- Bornovalova MA et al., 2008
- John OP, Gross JJ, 2004
- Lopes PN et al., 2005
- Hayes SC et al., 2006
- Richards JM, Gross JJ, 2000
- Linehan MM et al., 2006
- Silk JS et al., 2003
- Neacsiu AD et al., 2010
- Webb TL et al., 2012
- Berking M, Whitley B, 2014
- Cloitre M et al., 2012
- van der Kolk B, 2014
- Kabat-Zinn J, 2003
- Koerner K, 2012
- Hofmann SG et al., 2012
- Gratz KL, Roemer L, 2004
- American Psychological Association, 2020
- World Health Organization, 2019