Dr Ahsan Tariq , MBBS, MRCP (UK ) ongoing, IMT ( Internal Medicine Trainee, NHS England), GMC : 7805049
Dr Ahsan Tariq is a UK-registered medical doctor with a background in internal medicine and a focus on evidence-based research in cognitive health and nootropics. He critically reviews scientific studies, supplements, and ingredients to help readers make informed, safe, and effective choices for brain health and performance.
Introduction
Mineral deficiencies are becoming a silent global crisis. Despite having more access to supplements and nutrition information than ever before, millions of people continue to lack essential minerals without knowing it. According to the World Health Organization, over 2 billion people suffer from nutrient deficiencies worldwide [1]. Mineral shortages weaken immunity, drain energy, slow healing, and may even disrupt mental health.
This blog explores the hidden dangers, warning signs, and powerful fixes for mineral deficiencies in 2026 backed by scientific studies and expert insights.
What Are Mineral Deficiencies?
Mineral deficiencies occur when the body lacks sufficient levels of essential minerals needed for biochemical reactions. Minerals cannot be made by the body; they must come from diet or supplements.
Types of Essential Minerals
Minerals are divided into:
1. Macro Minerals (needed in larger amounts)
- Calcium
- Magnesium
- Sodium
- Potassium
- Phosphorus
2. Trace Minerals (needed in smaller doses)
- Iron
- Zinc
- Iodine
- Copper
- Selenium
- Manganese
- Chromium
Even trace minerals, though required in tiny amounts, are critical for hormonal balance, enzyme activity, immunity, detoxification, and brain function [2].
Why Mineral Deficiencies Are Increasing in 2026

Despite improvements in global nutrition awareness, deficiencies continue to rise. The reasons are more complex than “poor diet” alone.
1. Modern Farming & Soil Mineral Depletion
Over-farming, chemical fertilizers, and poor soil regeneration have reduced natural mineral levels. FAO reports that today’s soil contains 20–70% fewer minerals than it did decades ago [4].
2. Ultra-Processed Food Consumption
A study published in BMJ Nutrition found that ultra-processed foods contribute over 60% of daily calories for many people, yet contain almost no minerals [3].
3. Chronic Stress & Fast-Paced Lifestyles
Stress rapidly drains magnesium, potassium, and zinc due to increased cortisol and adrenaline release [5].
4. Gut Health Issues
Inflammation, antibiotic use, and poor microbial diversity reduce nutrient absorption significantly [26].
5. Medications That Reduce Absorption
- Antacids block magnesium and iron absorption
- Diuretics flush potassium
- Birth control pills reduce zinc levels [6]
6. Low Sunlight Exposure
Reduces Vitamin D synthesis, affecting calcium metabolism [7].
7. Highly Filtered Water
Modern filtration removes contaminants and essential minerals like calcium and magnesium [20].
Key Minerals & Their Roles
Understanding how each mineral works helps identify symptoms early.
Magnesium
- Supports 300+ biochemical reactions [8]
- Needed for muscle relaxation, sleep, nerve signals
- Deficiency causes cramps, anxiety, heart rhythm issues
Iron
- Required for hemoglobin and oxygen transport [9]
- Deficiency leads to anemia, shortness of breath, dizziness
Zinc
- Essential for immunity, hair growth, hormones [10]
- Deficiency weakens immunity, slows wound healing
Calcium
- Needed for bones, muscles, heart rhythm [11]
- Low levels cause tingling, muscle spasms
Potassium
- Regulates electrolytes, fluid balance, nerve activity [12]
- Low levels cause irregular heartbeats and muscle weakness
Hidden Dangers of Mineral Deficiencies
Most mineral imbalances develop silently.
1. Immune System Breakdown
Low zinc, selenium, and iron reduce white blood cell activity [13].
2. Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
Low iron, magnesium, potassium, and copper are linked with constant tiredness [14].
3. Hormonal Disruption
Iodine deficiency affects thyroid hormones, causing weight gain and brain fog [16].
4. Mental Health Problems
Magnesium and zinc deficiencies are linked to anxiety and depression [15].
5. Heart Health Risks
Potassium and magnesium deficiencies increase arrhythmia risk [12].
6. Bone Weakness
Low calcium + low magnesium accelerate bone loss [17].
7. Reproductive Problems
Zinc and iron imbalances affect fertility and menstrual health [29].
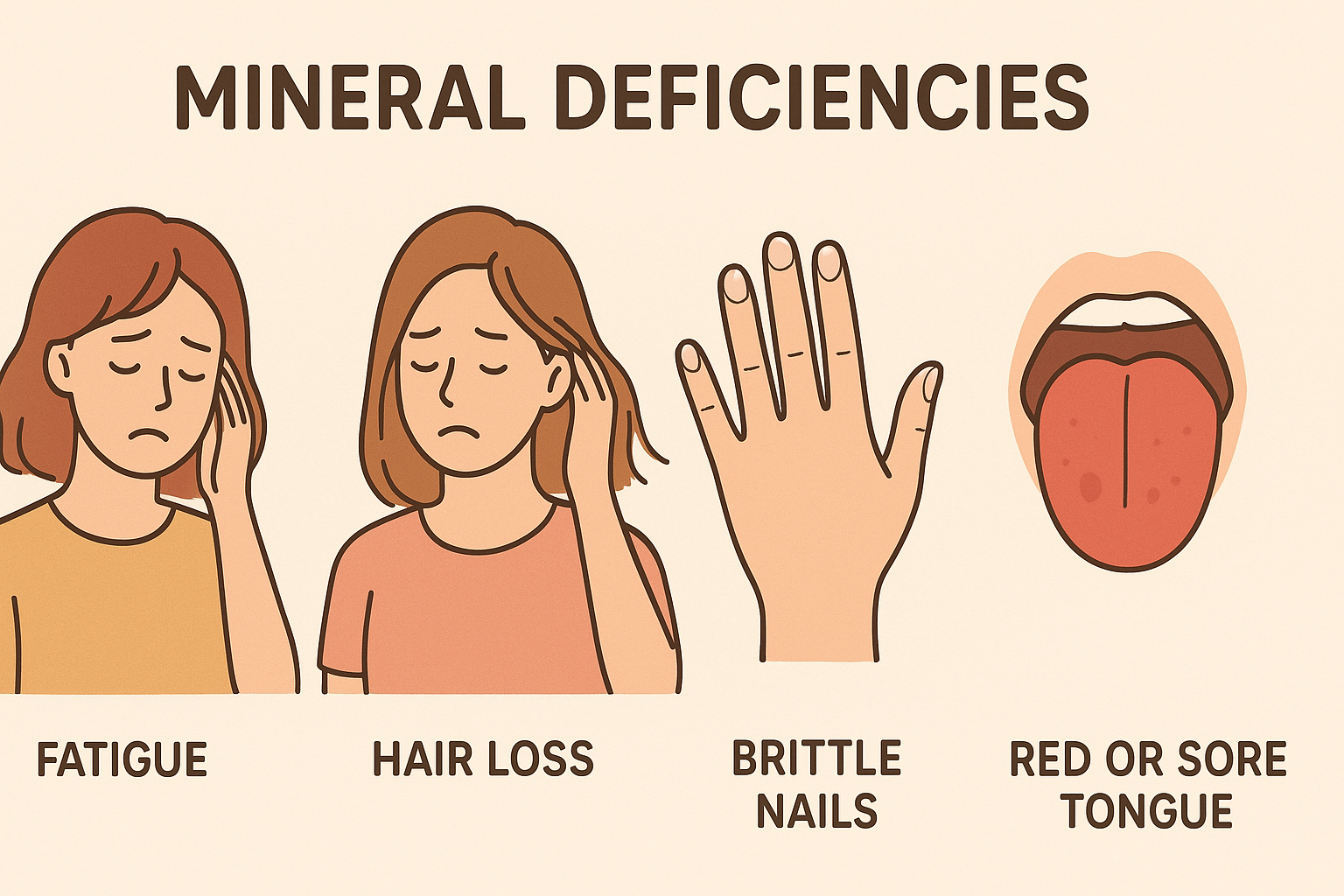
Common Symptoms You Should Never Ignore
Mineral deficiencies often mimic other health conditions.
Physical Symptoms
- Constant tiredness
- Muscle cramps
- Pale skin
- Weak nails
- Hair loss
- Irregular heartbeat
- Cramps and spasms
- Mouth sores
Mental Symptoms
- Irritability
- Anxiety
- Poor focus
- Sleep problems
A study found mild magnesium deficiency can cause significant neurological changes even before lab tests detect it [18].
Top Deficiencies in 2026 (Updated & Expanded Table)
| Mineral | Deficiency Rate 2026 | Risk Groups | Primary Causes | Major Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iron | 30% | Women, teens | Blood loss, low intake [19] | Fatigue, pale skin |
| Magnesium | 50% | Adults, stressed individuals | Diet, stress [20] | Anxiety, cramps |
| Zinc | 20% | Teens, vegans | Low meat intake [21] | Weak immunity |
| Calcium | 25% | Older adults | Low Vitamin D [22] | Weak bones |
| Iodine | 15% | Pregnant women | Low seafood [23] | Thyroid issues |
| Selenium | 12% | Low soil areas | Poor soil levels | Weak antioxidant system |
| Potassium | 10% | High sodium consumers | Diuretics | Heart irregularities |
Powerful Fixes to Restore Mineral Balance
1. Improve Diet Quality
Whole foods offer better absorption than supplements.
A diet rich in leafy greens, nuts, whole grains, and proteins significantly reduces deficiencies [24].
2. Reduce Chronic Stress
Stress-management techniques like mindfulness, movement, and sleep help restore magnesium and potassium levels [25].
3. Heal the Gut First
Poor digestion = poor absorption.
Fix with:
- Probiotics
- Fiber
- Fermented foods
- Limiting antibiotics
Research shows improved gut health increases mineral absorption by up to 30% [26].
4. Use High-Quality Supplements When Needed
Supplements help only when tests confirm deficiency [27].
Best forms:
- Magnesium glycinate or citrate
- Iron bisglycinate
- Zinc picolinate
- Calcium citrate
Avoid mega-doses; toxicity is possible [28].
5. Balance Electrolytes
Potassium, sodium, and magnesium must be balanced.
Electrolyte imbalance causes dehydration and irregular heartbeat.
Best Foods Rich in Essential Minerals
Magnesium Sources
- Spinach
- Pumpkin seeds
- Almonds
- Avocado
Iron Sources
- Lentils
- Eggs
- Red meat
- Spinach
- Chickpeas
Zinc Sources
- Yogurt
- Chickpeas
- Cashews
- Eggs
Calcium Sources
- Yogurt
- Broccoli
- Almonds
- Sardines
Potassium Sources
- Bananas
- Sweet potatoes
- Coconut water
Mineral Deficiencies in Age Groups
Teens
Growth spurts increase mineral needs dramatically.
Low zinc and iron are most common [29].
Adults
Stress, caffeine, and busy lifestyles drain magnesium, zinc, and potassium [30].
Older Adults
Absorption decreases with age; low stomach acid reduces mineral uptake [31].
Testing for Mineral Deficiency
Most Accurate Tests
- Blood serum test
- Ferritin test for iron
- RBC magnesium test
- Thyroid panel for iodine-related issues
Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute notes blood tests remain the gold standard [32].
Conclusion
Mineral deficiencies affect billions of people silently influencing mood, energy, immunity, hormones, and heart health.
The good news is that with the right diet, stress reduction, gut care, and strategic supplementation, deficiencies can be fully reversed.
Awareness is the first step. Action brings the real change.
References
- World Health Organization – Global Nutrition Data
- National Institutes of Health – Mineral Functions
- BMJ Nutrition – Ultra-Processed Foods Impact
- FAO – Soil Mineral Decline
- Stress & Nutrition Study, 2020
- Journal of Clinical Pharmacology – Medication Absorption Effects
- Endocrine Society – Vitamin D & Calcium Metabolism
- NIH Magnesium Fact Sheet
- WHO Iron Deficiency Report
- Journal of Immunology – Zinc’s Role
- American Bone Health Foundation
- Heart Rhythm Society
- Selenium and Immunity – Nutrition Research
- Iron Deficiency Fatigue Study – 2021
- Magnesium & Anxiety – Journal of Psychiatric Research
- Thyroid Iodine Study – Endocrine Reviews
- Calcium & Bone Density – JAMA
- Magnesium Neurological Study – Journal of Nutrition
- Global Iron Deficiency Data – UNICEF
- Magnesium Deficiency Review – Harvard Health
- Zinc Absorption Research – Nutrition Journal
- Vitamin D and Calcium Absorption – Mayo Clinic
- Iodine Deficiency Global Statistics – WHO
- Nutrient-Dense Diet Benefits – Dietetics Review
- Sleep & Stress Recovery Study – Sleep Medicine
- Gut Health & Mineral Absorption – Gut Microbiome Research
- Harvard School of Public Health – Supplement Use
- Mineral Toxicity Case Reviews – Toxicology Reports
- Teen Nutrition Status – American Academy of Pediatrics
- Adult Nutrition Report – CDC
- Aging & Nutrient Absorption – Geriatrics Journal
- Serum Mineral Testing – Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute


2 thoughts on “Mineral Deficiencies: Hidden Dangers & Powerful Fixes 2026”